Trading psychology Indonesia: When Indonesian beginners enter the markets, their focus often lies solely on charts, technical indicators, or trading signals. Yet within weeks or months, many find the real battle isn’t with price action—it’s with their own thoughts. Trading psychology Indonesia isn’t just a buzz phrase; it’s the architecture of how decisions are made under pressure. Emotional consistency—avoiding panic sells or impulsive buys—can be more impactful than any strategy. Studies in behavioral finance confirm that traders exposed to peer comparisons (for example, watching leaderboards) tend to take riskier actions and experience lower satisfaction—despite similar returns. Understanding one’s emotional triggers and how they influence trading patterns is therefore essential, more so in a fast-moving local market where sentiment shifts quickly.
Tracking Emotional Trends with Journals and Mindfulness

Source: Tradervue
A structured trading journal is more than just a record-keeping tool—it’s a mirror into your emotional habits. Recording trade rationale, your thoughts at entry/exit, and how you felt before and after can uncover hidden triggers like revenge trading or hesitation after losses. Weekly reviews of your journal help identify when anxiety spikes or confidence wavers. Combined with brief mindfulness exercises—such as deep breathing or short meditation breaks—you build emotional resilience that moderates reactions during volatile market swings. Indonesian traders who integrate this practice into their routine report more neutral responses to familiar market stressors.
Trading psychology Indonesia: Recognizing and Counteracting Cognitive Biases
Common cognitive biases such as gambler’s fallacy, confirmation bias, anchoring, and herd mentality quietly distort rational thinking. For instance, expecting a rebound simply because prices have dropped steadily reflects gambler’s fallacy, while holding onto a losing trade due to hope showcases loss aversion and anchoring bias. Many traders post-rationalize trades by selectively recalling data that supports their initial belief—confirmation bias in action. By journaling and periodically challenging your assumptions—for example, asking yourself whether you’re seeking contrary evidence—you weaken the grip of these biases and foster more objective decision-making.
Trading psychology Indonesia: Emotional Peaks & Market Behavior Patterns
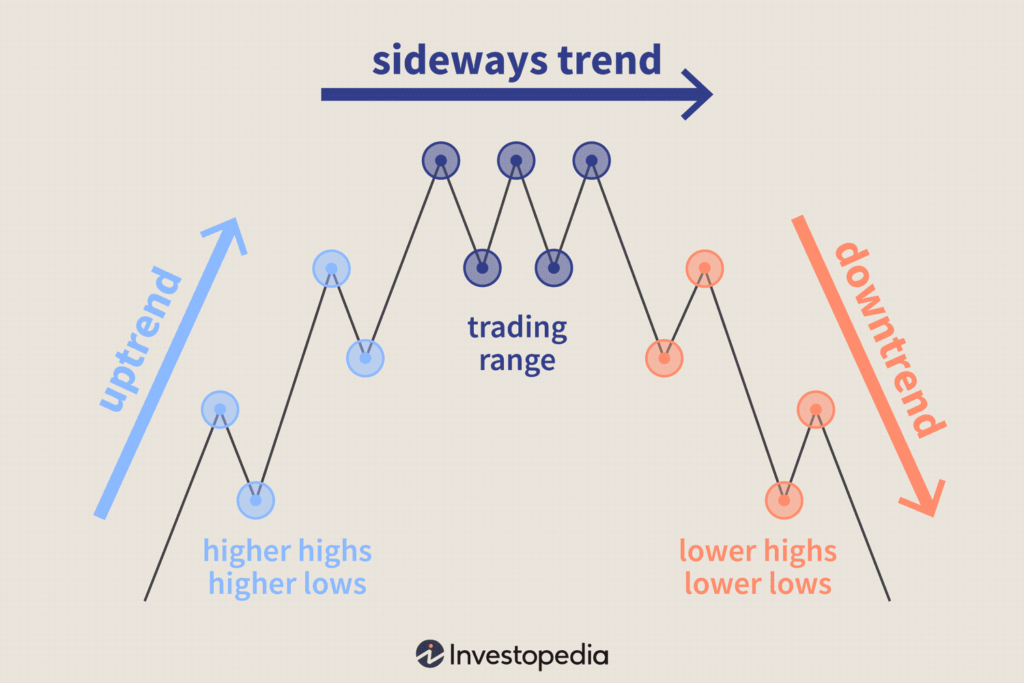
Source: Investopedia
Trend analysis in trading psychology reveals that emotions follow predictable peaks. Initial overconfidence often plummets into anxiety when trades underperform; after losses, fear of further drawdown might cause hesitation or refusal to cut losses (disposition effect). Moreover, when traders face a loss, they are often unwilling to realize it, leading to emotionally driven holding of bad positions. Recognizing these emotional rhythms—especially after several consecutive results—can guide you to adopt preventive measures, such as pausing trading after big wins or refraining from action during emotional slumps.
Trading psychology Indonesia: Techniques to Enhance Psychological Resilience
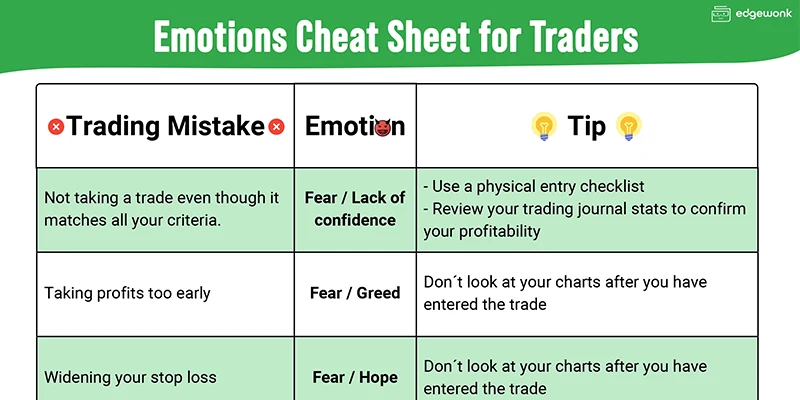
Source: edgewonk
Building emotional strength requires deliberate actions:
- Volatility Protocols: Automate stops and limits, set performance alerts, and schedule breaks when volatility spikes to avoid impulsive decision-making .
- Pre‑Trade Checklists: Ask yourself before execution: “Does this trade fit my rules? Am I calm? Is this FOMO‑driven or calculated?” These prompts curb hasty emotional trades.
- Retrospective Emotional Mapping: In post‑trade review, label biases such as anchoring or overconfidence. This awareness helps you create corrective habits.
For Indonesian traders, formalizing these routines brings emotional trends into view, turning them from hidden obstacles into strategic allies.
Applying the Mind–Method–Money Framework
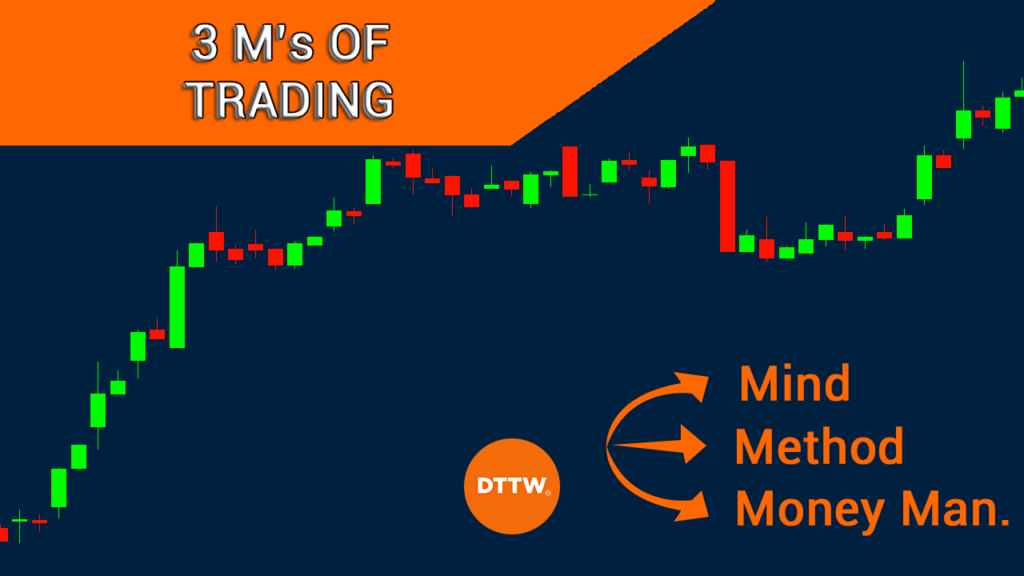
Source: Real Trading
A balanced trading approach requires integration of all three pillars:
- Mind: Your emotional clarity, self-awareness, and bias control.
- Method: A tested, rule-based strategy—unchanged by short‑term feeling.
- Money: Risk allocation and position sizing driven by logic—not by ego or anxiety.
Neglecting the “Mind” pillar often leads to poor adherence to strategy or poor risk control. Regularly evaluating all three ensures emotional shifts don’t stealthily undermine your trading foundation.
Avoiding Crowd Traps and Social FOMO
Social media and trading platforms amplify peer influence, pushing traders into trend-chasing behavior. Seeing others profit from hot trades often triggers FOMO and hasty entries without analysis. Over time, these impulsive trades can erode capital and discipline. Research advises that avoiding comparison-driven decisions and staying anchored to your own performance benchmarks—rather than chasing others—builds emotional stability and long‑term consistency.
Final Thoughts: Making Emotional Awareness a Competitive Edge
In conclusion, Trading psychology Indonesia isn’t a theoretical add-on—it’s the lens through which all trading decisions are filtered. By tracking emotional trends, recognizing bias, using structured tools like journals and checklists, and balancing the Mind‑Method‑Money framework, beginner traders can transform psychological vulnerabilities into actionable strengths. Emotional fluency becomes a sustainable edge, enabling better consistency, reduced stress, and long‑term performance in Indonesia’s dynamic markets.











